Backgammon
Impostazione
Il backgammon è un gioco per 2 giocatori. E' giocato su una tavola costituita da 24 triangoli di colore alternato, chiamate punti. La tavola è divisa in quattro quadranti di sei punti ciascuno, casa e fuori per ciascun giocatore. La casa ed il fuori sono separati dagli altri da una divisione centrale chiamata sbarra. Ogni giocatore ha 15 pezzi del suo colore, generalmente chiamate come pedine.
La posizione iniziale delle pedine e la direzione di gioco sono mostrate qui di seguito:
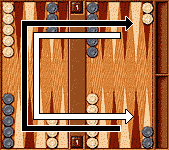
Entrambi i giocatori hanno il loro paio di dadi. Un cubo per il raddoppio, con i numeri 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, e 64, è anche usato per tenere una traccia dell'attuale situazione della partita.
Obiettivo del gioco
L'obiettivo del gioco è per il giocatore di portare tutte le sue pedine dentro la sua casa e poi tirarle fuori. Il primo giocatore che riesce a farlo vince la partita.
Movimenti
Un giocatore lancia due dadi e due numeri appaiono e costituiscono le due mosse da effettuare. Lui può farle entrambe sulla stessa pedina, oppure effettuarle su due pedine diverse. Ci sono 3 tipi di mossa legale:
- muovere una pedina avanti del numero corrispondente ad un dado per ogni triangolo;
- fare entrare una pedina dalla sbarra al punto opposto della casa corrispondente al numero sul dado;
- Mandare fuori una pedina se tutte le altre sono già entrate nella casa.
Un giocatore non può muovere la sua pedina in un punto già occupato da due o piu' pedine avversarie (punto bloccato).
Un giocatore che, lanciando i dadi, effettua due doppi dadi gioca i numeri mostrati sui dadi due volte. Per esempio, se ha lanciato un 5-5, lui gioca quattro 5 utilizzando qualsiasi combinazione a sua scelta, che soddisfino le regole citate.
Un giocatore deve giocare entrambi i numeri del lancio di dadi effettuato se possibile. Se non puo' muovere una pedina dovra' utilizzare il numero piu' alto mostrato dai dadi.
Blots
Una singola pedina in un punto e' chiamata blot. Un blot puo' essere mangiato e rimandato al punto di partenza.
Bearing Off
When a player has brought all of his 15 men into his home board, he can commence bearing off. In bearing off, a player removes men from the points corresponding to the roll. If the number on the die is higher than the highest point on which the player has a man, he may bear off man from his highest occupied point. Men borne off are not re-entered into play. A player, however, may not bear off men while he has a man on the bar, or outside his home board. Thus if, a man was hit during the process of bearing off, the player must first re-enter it and bring it around into his home board before he can continue the bearing off process.
Doubling
Before the player rolls the dice to start his turn, he can offer to double the current stakes by turning the doubling cube to 2 if it's the first double in the game, or to the next value of the sequence 2, 4, 8,16 etc. if it's a redouble. The opponent may refuse the double in which case he forfeits the game at the current stake or he may accept the double. The player who accepts the double becomes the owner of the cube and only he can make the next double. Matches are normally played using the Crawford rule, which forbids doubling in some cases (see Match Rules).
Scoring
At the end of the game, if the losing player has borne off at least one checker, he loses the single value of the game as shown on the doubling cube (one point, if thef the loser has not borne off any men then the winner won gammon and receives twice the value of the doubling cube. If the loser has not borne off any men and still has one or more men on the bar or in the winner's home board then the winner won backgammon and receives three times the value of the doubling cube.
Optional rules
The following rules are used as optional:
- The Jacoby Rule. Gammons and backgammons are not scored as such if neither player doubled during the course of the game. By default this rule is disabled in all game variations except Hypergammon.
- Beavers. When a player doubles, his opponent may immediately redouble (beaver) while retaining possession of the doubling cube. By default this rule is not used.
- Automatic doubles. If both players roll the same number on the first roll of a game, game stake is doubled. By default this rule is disabled.
Match rules
Matches are played using Crawford rule. It states that if one player is one point from winning the match, doubling is disallowed in the next game. This one game without doubling is called the Crawford game. Once the Crawford game has been played, if the match has not yet been decided, the doubling is allowed in all remaining games of the match.